Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O in the film on Fe oxidized at high temperature in air
O in the film on Fe oxidized at high temperature in airHaruna, Takumi*; Yamamoto, Tatsuya*; Miyairi, Yoji*; Shibata, Toshio*; Taniguchi, Naoki; Sakamaki, Keiko; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 64(5), p.201 - 206, 2015/05
Diffusion coefficients of D O in the films was determined in order to estimate corrosion rate of carbon steel for the overpack in ground water. Fe plates were heated to form oxide films. The films were characterized with XRD and SEM. After that, the specimen was contacted with D
O in the films was determined in order to estimate corrosion rate of carbon steel for the overpack in ground water. Fe plates were heated to form oxide films. The films were characterized with XRD and SEM. After that, the specimen was contacted with D O for 5184 ks, followed by subjected to TDS to obtain an amount of D
O for 5184 ks, followed by subjected to TDS to obtain an amount of D O absorbing into the film. As a result, single-layered film of Fe
O absorbing into the film. As a result, single-layered film of Fe O
O was formed at 573 and 723 K, and double-layered film of Fe
was formed at 573 and 723 K, and double-layered film of Fe O
O and Fe
and Fe O
O was formed at 873 K. It was found that an amount of D
was formed at 873 K. It was found that an amount of D O in the film correlated linearly with a square root of the absorption period, and that the amount was steady for a long period. From the results and Fick's second law, diffusion coefficients of D
O in the film correlated linearly with a square root of the absorption period, and that the amount was steady for a long period. From the results and Fick's second law, diffusion coefficients of D O was determined as 9.7
O was determined as 9.7 10
10 cm
cm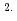 s
s for the Fe
for the Fe O
O film, and 5.5
film, and 5.5 10
10 cm
cm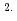 s
s to 2.2
to 2.2 10
10 cm
cm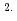 s
s for Fe
for Fe O
O film.
film.
 -ray irradiation; Effect of chloride ion concentration
-ray irradiation; Effect of chloride ion concentrationMotooka, Takafumi; Yonekawa, Kazuo; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
no journal, ,
It is known that the corrosion of steel in neutral chloride solution has a chloride concentration at which the corrosion rate reaches a maximum. However, it is unknown that the effect of radiation at a low dose rate on this phenomenon. Therefore, we examined the effect of radiation at a low dose rate on corrosion of steel in neutral chloride solution by corrosion tests using various concentration of chloride neutral solutions. As the results, the corrosion rate becomes a maximum at a certain chloride concentration. It is consider that the increase in conductivity of solutions along with the chloride concentration increases and the decrease in concentrations of hydrogen peroxide and dissolved oxygen are key factors for the corrosion of steel in neutral chloride solution under a low dose rate condition.
Shibata, Toshio*; Taniguchi, Naoki; Sakamaki, Keiko; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*
no journal, ,
Carbon steel has been selected as a candidate material for the overpack and its corrosion behavior has been studied. The corrosion model of carbon steel in the oxygen depleted environment has been developed in case of a magnetite (Fe O
O ) corrosion film formed on the steel surface by assuming that diffusion of H
) corrosion film formed on the steel surface by assuming that diffusion of H O through the corrosion film controls the corrosion process. The improved model which includes the dissolution of the magnetite film has been proved successfully to predict the corrosion rate after a long exposure term. This study aims to simulate the corrosion behavior of carbon steel forming the siderite (FeCO
O through the corrosion film controls the corrosion process. The improved model which includes the dissolution of the magnetite film has been proved successfully to predict the corrosion rate after a long exposure term. This study aims to simulate the corrosion behavior of carbon steel forming the siderite (FeCO ) corrosion film and compare with the behavior of the magnetite film case. Based on the experimental results reported, the corrosion rate was estimated for two cases of 0.1 M and 0.25 mM of the total carbonate and compared with the experimental results. It was concluded that the siderite film formed more likely in the 0.1 M than 0.25 mM solution.
) corrosion film and compare with the behavior of the magnetite film case. Based on the experimental results reported, the corrosion rate was estimated for two cases of 0.1 M and 0.25 mM of the total carbonate and compared with the experimental results. It was concluded that the siderite film formed more likely in the 0.1 M than 0.25 mM solution.
Taniguchi, Naoki; Kawasaki, Manabu*; Sugita, Yutaka; Shibata, Masahiro; Honda, Akira
no journal, ,
Carbon steel is one of the candidate materials for overpacks of geological disposal of high level radioactive waste, and it is important to understand the corrosion behavior of carbon steel in repository environment. Initially, the buffer material composed of mainly bentonite will contain moisture depending on ambient humidity. The water content in buffer material will be increased with time due to the infiltration of groundwater. The oxygen in buffer material brought form the ground will be consumed by the reaction with minerals in bentonite and corrosion of overpack, and then low oxygen condition will be achieved around the overpack. The corrosion behavior of overpack will be varied with the change of environmental conditions during water saturation process of buffer material. In this study, a corrosion sensor was developed to monitor the change of corrosion behavior (corrosion potential and corrosion rate) with changing of the environmental conditions in buffer material. Using a prototype of the sensor, change of corrosion of carbon steel was monitored actually in buffer material in the process of saturation.
Shimizu, Kosuke*; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Taniguchi, Naoki; Sakamaki, Keiko; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*
no journal, ,
The effect of solution pH to the SCC susceptibility of carbon-steel (CS) in an anaerobic ground water must be investigated to guarantees the soundness of the CS HLW overpack for ultra-long term. For the present study, the SCC susceptibility of CS at and near the reversible hydrogen evolution potentials at each solution pH was evaluated by the slow strain rate test (SSRT); as for the test solution, NaHCO /Na
/Na CO
CO solutions whose pH were adjusted 8 to 13 and purged with Ar gas were used. The SCC susceptibility became minimum at pH near 9 and 13 as well as reached maximum at pH near 11.
solutions whose pH were adjusted 8 to 13 and purged with Ar gas were used. The SCC susceptibility became minimum at pH near 9 and 13 as well as reached maximum at pH near 11.
Soma, Yasutaka; Kato, Chiaki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
no journal, ,
Within crevice of austenitic stainless steel (solution treated, mirror poloshed) immersed in high-temperature water (561K, 8.5MPa, dissolved oxygen conc. 32ppm, conductivity ca.1 to 1.5e-6S/cm), new form of intergranular oxidation was occured. The intergranular oxidation occured in certain area within the crevice, that is, the area with relatively low crevice gap and distant from the crevice mouth. Cr was enriched in the oxide and the oxidation occured both grain boundary and grain matrix. After the intergranular oxidation, some grain was loosen and peered off. Maximum depth of the intergranular oxidation was 50e-6m/500h. Because almost no stress was applied on the specimen, relationship between this oxidation bahavior and stress corrosion cracking should be clarified by further experiment.
Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Irisawa, Eriko; Abe, Hitoshi
no journal, ,
The reprocessing components made of stainless steel appear intergranular corrosion in boiling nitric acid solution containing high oxidizing metal ions derived from spent nuclear fuel. In this paper, to clarify the corrosion mechanism in this environment, temperature dependence of corrosion rate of a stainless steel in boiling 3 molar nitric acid with added pentavalent vanadium was studied. As the results of investigation of the temperature dependence of the corrosion rate of the heat transfer surface using estimated temperature from a boiling curve, it was found that there was no effect of heat flux on corrosion rate because the dependence was consistent between heat transfer condition and non-heat-transfer. Also it was found that the activation energy was different between the boiling conditions of about 378 K or more and the non-boiling conditions of below 378 K.
Irisawa, Eriko; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Abe, Hitoshi; Kumagai, Mikio*; Suzuki, Kazunori*; Hayashi, Shinichiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Komatsu, Atsushi; Nakano, Junichi*; Tsukada, Takashi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
no journal, ,
Seawater was injected into the reactor core in Fukushima 1st nuclear power plant for emergency cooling. Therefore it is concerned that primary containing vessel will corrode faster under irradiation in salt containing condition than usual. Corrosion rate of carbon steel in neutral water containing chloride ion is controlled by diffusion of dissolved oxygen. However hydrogen peroxide generated under  ray irradiation will accelerate corrosion. In this study, diffusion coefficient and the thickness of diffusion layer for oxygen and hydrogen peroxide were measured to simulate corrosion rate of carbon steel. The ratio of diffusion limiting current density for hydrogen peroxide by oxygen was about 0.39 in the same concentration. Corrosion test was conducted and the result was compared to the simulation.
ray irradiation will accelerate corrosion. In this study, diffusion coefficient and the thickness of diffusion layer for oxygen and hydrogen peroxide were measured to simulate corrosion rate of carbon steel. The ratio of diffusion limiting current density for hydrogen peroxide by oxygen was about 0.39 in the same concentration. Corrosion test was conducted and the result was compared to the simulation.
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationInoue, Hiroyuki*; Hata, Kuniki; Idehara, Ryuichi*; Kojima, Takao*; Kasahara, Shigeki; Iwase, Akihiro*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English